Although pressure sensors and pressure transmitters are similar in name, they are very different in their respective application fields; their structure and composition are quite different.
The pressure sensor is the most commonly used sensor in industrial practice. It is widely used in various industrial automation environments, including water conservancy and hydropower, railway transportation, intelligent buildings, production automation, and aviation Aerospace, military, petrochemical, oil well, electric power, shipbuilding, machine tools, pipelines and many other industries.
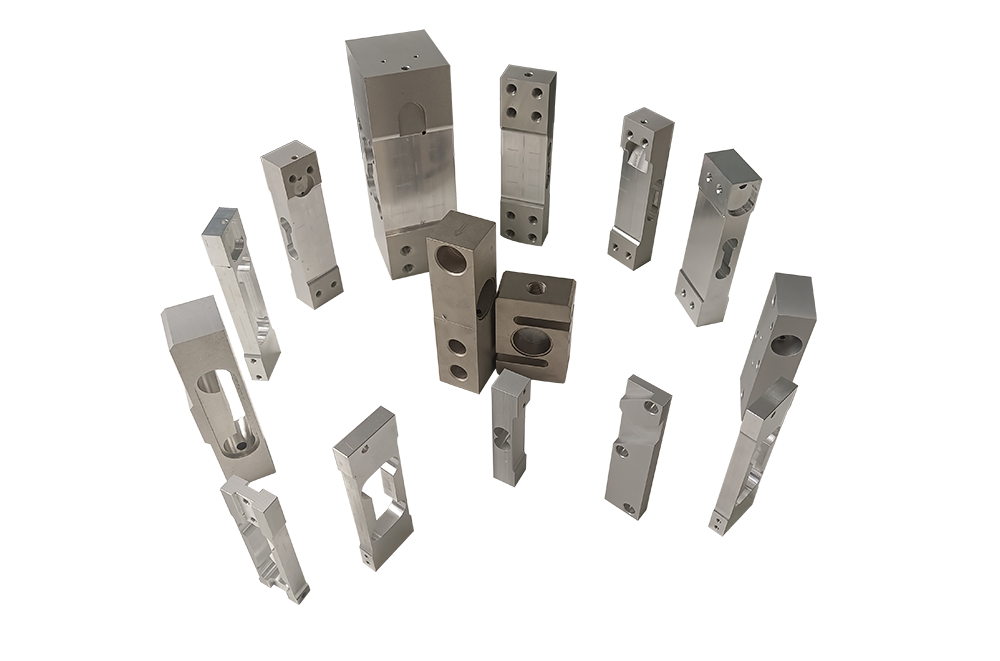
The pressure transmitter is mainly composed of three parts: load cell sensor, measuring circuit and process connection. It is widely used in petrochemical, electric power, city gas, pulp and papermaking, machinery, shipbuilding and other industries.
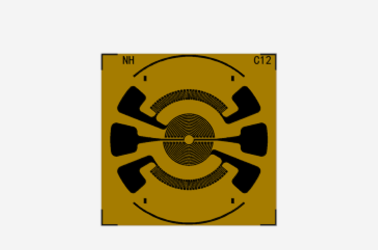
Pressure sensors usually specifically refer to component-level products with non-standard mV signal output. They are the core components of pressure transmission. Due to the non-standard nature of the signals, users need to perform pressure calibration when using them. And design a special signal processing circuit; because the signal is weak, an amplifier needs to be added when the distance is long;
The pressure transmitter is also a pressure sensor in the written sense, but its output signal is a standard and common signal, such as 4~20mA, 1~5V, etc., which can be transmitted over a long distance .